Cybersecurity has never been more crucial. Between January 1, 2005, and May 31, 2020, 11,762 intrusions were recorded. Customers want to know that their data and personal information are protected, regardless of whether you are training various customers and organizations or selling commercial training. For example, customers enrolled in training programs do not want their data shared with third parties.
Choosing the incorrect LMS provider could cost employees their employment if the proper security measures are not in place when a data breach or cyberattack occurs.
Content Outline
- What is LMS?
- Authenticated by 2-step verification
- IP Blocker
- SSL
- Enhanced Password Verification
- Domain-Based Enrollments
- Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Back-Up Data Storage
- User Roles
- Mobile Security
- Conclusion
What is LMS?
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are online platforms that schools, businesses, and other groups use to offer and manage educational and training content. LMS platforms have delicate data like user credentials, academic records, and other private information that needs to be kept safe. LMS Security refers to the steps taken to protect an LMS platform from unauthorized entry, data breaches, and other security threats.
LMS software must be secure to protect users’ privacy and safety. When there is a security breach, sensitive information can be lost, the institution or organization’s image can be hurt, and there may be legal or financial consequences. Below are a few features that an LMS platform carry along with it.
Authenticated by 2-step verification

Two-factor authentication is one of the LMS’s most important yet neglected security features. Google’s report on ‘Account authentication and best practices’ indicates that multifactor authentication offers complete protection against automated assaults.
Two-factor authentication guarantees that only authorized users can access the learning management system. After entering their login credentials (usernames and passwords), the system will require users to provide additional proof of identity.
IP Blocker

IP blockers prevent access to your data by hostile or intrusive IP addresses. The administrator can explicitly add IP addresses to the “allowed” or “blocked” lists. This ensures that known virtual adversaries cannot view your user data or eLearning content without authorization via the LMS. The disadvantage is that they can always use a different IP address to circumvent the blockade, making it imperative to implement additional preventative LMS security measures.
SSL

Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is an encryption on a website that encrypts data and secures online communications. An encrypted link is created if SSL is enabled when a web browser (such as Google Chrome) connects to a website. SSL secures an internet connection and prevents sensitive data, such as credit card information, from being transmitted between systems or altered by unauthorized parties. It is necessary to buy SSL certificates nowadays to secure the site.
SSL should be enabled on your LMS and any LMS portals created for your consumers to protect everyone’s private information.
How do we know whether SSL is enabled? When a padlock appears next to a website’s URL.
Enhanced Password Verification
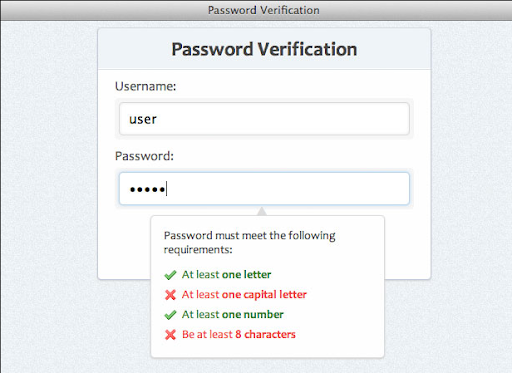
When users join into the LMS, their usernames and passwords are transferred as a single file to a remote access server. Additional protocols may be in place to guarantee that only authorized users can access the data.
For instance, online students are limited to three attempts before the system logs them out. This helps to prevent password guessing by hackers and other malicious sites. Sometimes, users must enter a code or display a prompt to prove they are human.
Domain-Based Enrollments
Online learning has become increasingly popular, and many organizations are turning to Learning Management Systems (LMS) to facilitate their training and development programs. One such LMS plugin that can be used for this purpose is the WordPress LMS Plugin by StylemixThemes.
However, it is important to note that for security purposes, online students can only register for the LMS via domains specified by the administrator. Using the WordPress LMS Plugin, you can set up a subdomain of your primary corporate website or a dedicated eLearning portal where students can register. Additionally, you can use password-protected domains to enhance LMS security further.
Using StylemixThemes’s plugin, you can ensure you have all the necessary and advanced features in your LMS portal.
Single Sign-On (SSO)

SSO enables users to use single credentials across all their applications. Using SSO, users can connect to the LMS with their work email address and password rather than memorize a new set of credentials. Companies who wish to manage their employees’ credentials commonly use single Sign-On. This is convenient and secure for businesses where each employee has a domain-specific email address.
Back-Up Data Storage

The system take backup of data timely while saving the latest version of eLearning content. Therefore, it remains secure even if your data is compromised by malware or inadvertently deleted for any reason. Remember that backup protocols vary depending on the LMS provider. Some may backup their data nightly and put it on a distributed storage service, but others may have dedicated servers.
User Roles
Users taking training classes should have less access to the platform than administrators and teachers in charge of it. For example, if a user finishes a test, they should not be able to change their final grade, and if they reply to a discussion board, they should not be able to grade themselves. Certain actions and duties in an LMS should be reserved for certain users.
Mobile Security

More and more online learners are switching to mobile devices, so your new LMS must have protection features for mobile devices. It includes encrypting data, authenticating mobile users, and protecting against viruses and spam. This is useful if you want to make a mobile app for learning anytime and anywhere.
Conclusion
When it comes to the security of both people and content, LMS security is paramount. Protecting a learning management system (LMS) from hacking can be accomplished largely through stringent security measures, including strong passwords, two-factor authentication, access controls, and SSL certificates.